Over the last decade, cloud computing has become one of the ideal trends to undertake business transformations and launch new innovations and infrastructures. It is a preferred solution for companies with offices at multiple locations and centralized data management is needed. Here is the basic guide of what cloud computing is, its types, benefits & a tad bit of everything you need to know.
What does Cloud Computing Literally Mean?
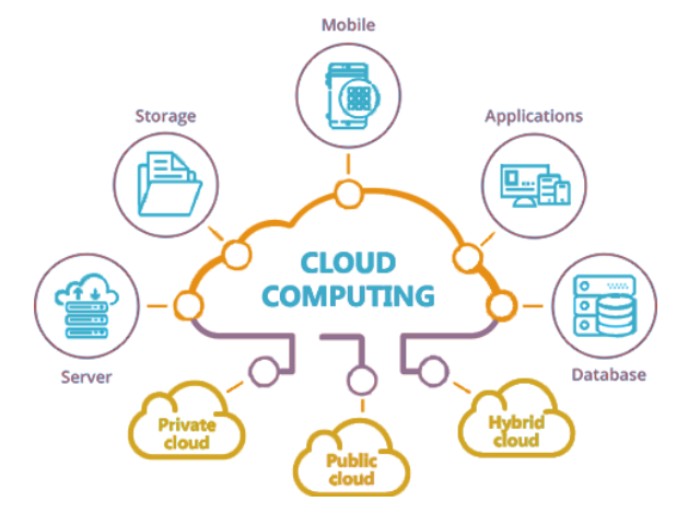
Simply put, cloud computing is a network of internet-hosted remote servers that deliver computing services — including servers, databases, storage, networking, information technology, organizing, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”). Cloud computing can be your virtual agent to dig for flexible resources, automotive processes, fast innovations and help organizations achieve economies of scale. You just pay cloud storage, space & data replication fee and it will help bring down your operating costs, run your infrastructure all the more proficiently and scale as your business needs change.
Cloud Computing: Benefits
The nature of doing business and its practices have substantially revolutionized since the last few years, so now organizations have been turning to cloud-based services. Cloud computing is a major move from the usual way organizations consider IT resources.
Here are the top benefits of cloud computing:
-
Cost
The use of cloud computing saves the capital cost for purchasing equipment, hardware and software and setting ready for nearby datacenters—the racks of servers, the up and running electricity supply and for power and cooling, the IT specialists for dealing with the foundation. It includes quick.
-
Worldwide Scale
The advantages of cloud computing services incorporate the nonstop provision of electricity. Once your cloud-based services are set up, now it’s not your headache to worry about perfect measure of IT resources—for example, power supply, storage capacity, data transfer speed and in addition to that, cloud knows when what is required and from the privileged geographic area.
-
Efficient & Productive Workflow
On location data centers normally require a great deal of “racking and stacking”— equipment arrangement, software fixing, and other tedious IT related errands. Here we have a solution to this i.e., cloud computing. It allows IT resources to invest their energy in accomplishing progressively significant business goals than the random chores.
-
Execution
Cloud computing services run on a worldwide network of safe and secure data centers. These service providers make sure that the computing hardware equipment is up-to-date and performs well. This is way more of a better option than a single corporate datacenter.
-
Unwavering Quality
Cloud computing services provide additional services such as data backup, disaster recovery and business congruity in a simpler and more affordable way. Your data is easy to access as it is replicated at multiple cloud locations on the cloud provider’s network. Although, the concerns for misuse of data might be a concern for most of the clients.
-
Fast & Secure
Many cloud suppliers offer a wide arrangement of strategies, innovations and controls that reinforce your security act by and large, ensuring your information, applications and framework from potential threats. Furthermore, these services are easy to buy with just a few clicks and transparent in their policies.
3 Ways to Deploy Cloud Computing Services
There are many types of cloud computing that must be carefully selected depending upon your business needs. To begin with, you have to decide the kind of cloud architecture on which your cloud services will be actualized. There are three unique approaches to deploy cloud-based services: on a public cloud, private cloud or hybrid cloud. Let’s check them briefly one-by-one.
-
Public cloud
The public clouds are owned and run by a third-party cloud-service provider, which provides the servers and storage facility over the internet. You get to these services by paying the fee and access it using a web browser.
Example: Microsoft Azure
-
Private cloud
A private cloud alludes to cloud computing services that are solely used and operated by a single company. The companies can own a physical on-site datacenter. A few organizations also pay third-party cloud networks to have their private cloud.
-
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid cloud is an amalgamation of both of the above, public and private clouds. It is bound together by technology that permits contents and applications to be shared between them. Hybrid cloud gives your business more prominent adaptability, greater innovation choices and infrastructure, security and consistency.
IaaS, PaaS, Serverless & SaaS – Types of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud computing services are broadly categorized into 4 types. Recognizing what they are and how they are different from one another, makes it simpler to achieve your business objectives.
-
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
This one is the most basic type of cloud-based service. As its name suggests, you rent out IT infrastructure, servers, virtual machines (VMs), storage, networks, operating systems—from a cloud provider on a pay-as-you-go basis.
-
Platform as a service (PaaS)
PaaS refers to an on-demand cloud computing service that allows developers to use a rented platform for developing, testing, managing and delivering Software apps. This is very helpful for software engineers and developers as they can easily manage and develop apps without worrying or setting up the basic infrastructure of servers, network, databases and storage required for development.
-
Serverless computing
Serverless computing basically overlaps with PaaS but it revolves around building app functionality without investing time and energy persistently dealing with the servers and infrastructure required to do as so. From server management, setup and capacity planning – everything is handled by service provider.
-
Software as a service (SaaS)
SaaS is a technique that comes in handy when dealing with the development and delivering web-based software applications on request and commonly on a subscription basis. With SaaS, cloud providers have to deal with the software management and underlying infrastructure. They also provide maintenance services such as software patching and upgrades.
